Early Inhalation Therapy Medications
Medications delivered by inhalation in the first four decades of the profession (1940s-1989) are featured.


Overview
DPIs, pMDIs, and inhalation solutions commonly used during the first four decades of the respiratory therapy profession are featured in this gallery and listed by release date.


1940s
Inhaled meds from the 1940s are featured.


Diluents
Normal saline, half-strength saline, and sterile distilled water were prescribed as diluents for medications delivered by IPPB and small volume nebulizers.
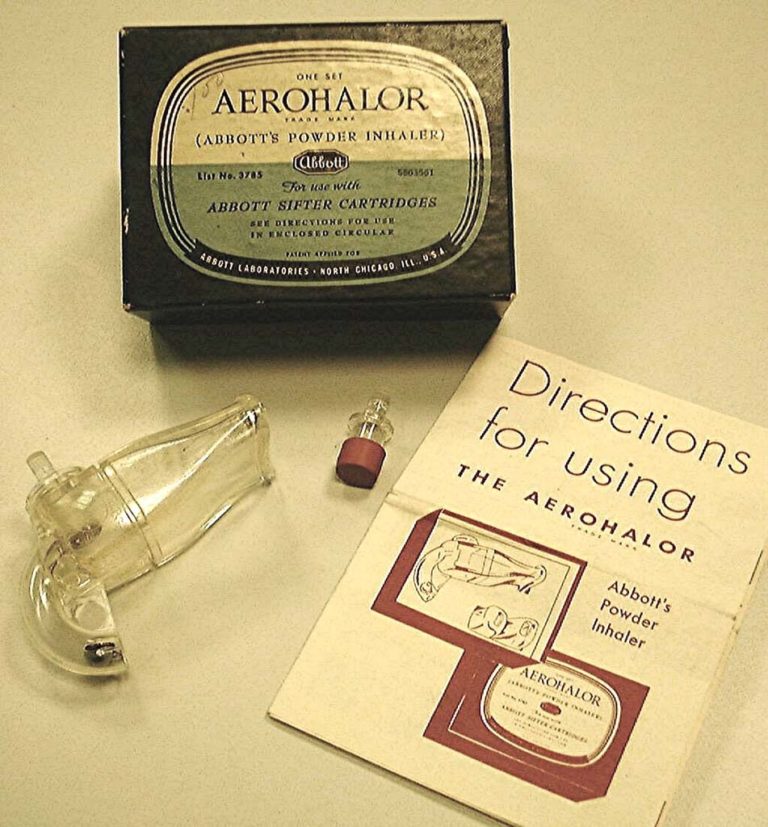
Penicillin DPI
Dr. Alvan Barach first reported on the administration of penicillin by inhalation in the early 1940s.
Penicillin G was the first agent administered as an inhaled dry powder. By the late 1940s, Abbott produced the Aerohaler which was designed to deliver penicillin G.
Penicillin G was the first agent administered as an inhaled dry powder. By the late 1940s, Abbott produced the Aerohaler which was designed to deliver penicillin G.
Image from Mark Sanders
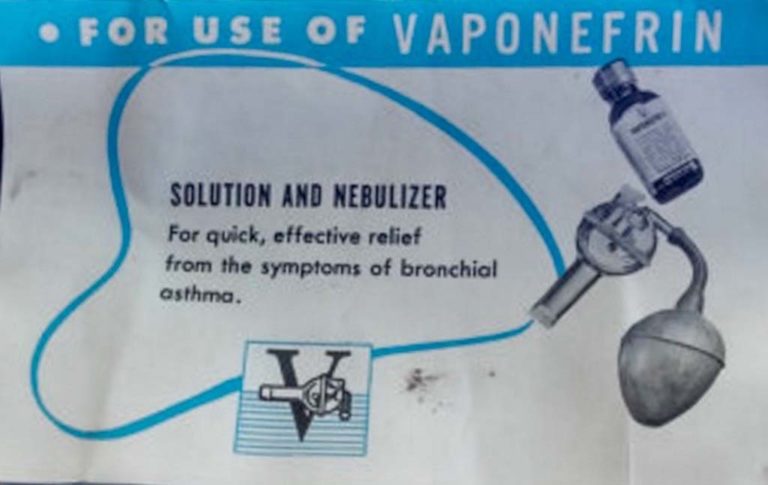

Vaponefrin (racemic epinephrine)
Vaponefrin was registered as a trademark in 1935.
Vaponefrin (racemic epinephrine) was nebulized and commonly administered in the treatment of upper airway edema and post-extrubation stridor.
Vaponefrin (racemic epinephrine) was nebulized and commonly administered in the treatment of upper airway edema and post-extrubation stridor.


1943 Patent
The formulation of the drug that would be released as "Isuprel" was patented in 1943.

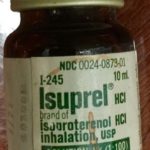
Isuprel
Isuprel (isoproterenol HCl) , was one of the first bronchodilators administered via IPPB.
Isuprel was trademarked in 1947.
Isuprel was trademarked in 1947.
Image from Felix Khusid


1940s Asthmanefrin ad
This ad for Asthmanefrin appeared in newspapers in the 1940s.
Image from Steve and Mary DeGenaro

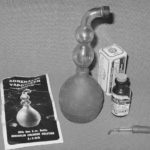
1947 Adrenalin Kit
This kit contained a solution of Adrenalin (1:100), a bulb glass nebulizer, a dropper, and instruction pamphlet.
Image from Mark Sanders


1950s
Respiratory medications from the 1950s are featured.


Vaponefrin ad from 1950s
This journal ad for the Vaponefrin (Racemic epinephrine) solution indicated that it was the "textbook therapy for emphysema, asthma, and chronic bronchitis."
Image from Felix Khusid
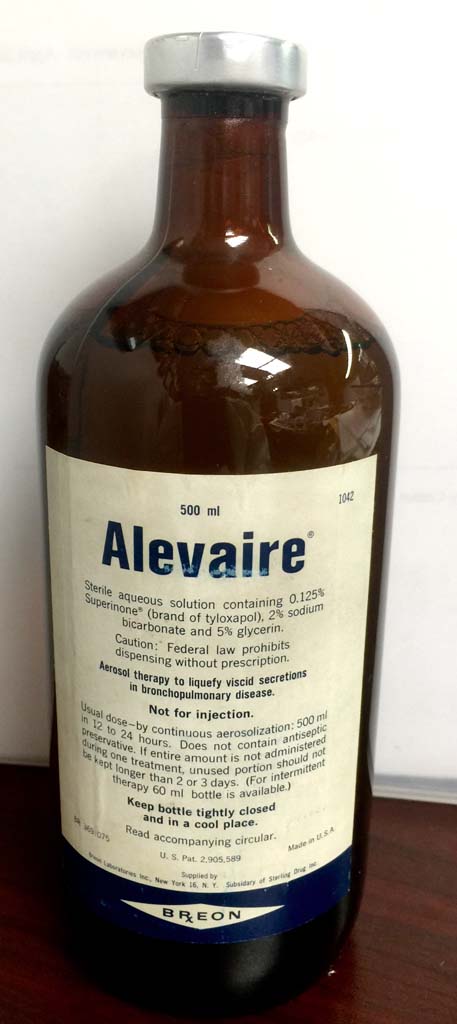

Alevaire
Alevaire, a solution of Superinone (tylaxopol), sodium bicarbonate, and glycerin, was a popular mucolytic in the 1950s-1970s.
Image from Felix Khusid


1955 Alevaire ad
Alevaire, described as a mucolytic in this 1955 ad, was designed for both intermittent use via IPPB and continuous nebulization in tents.
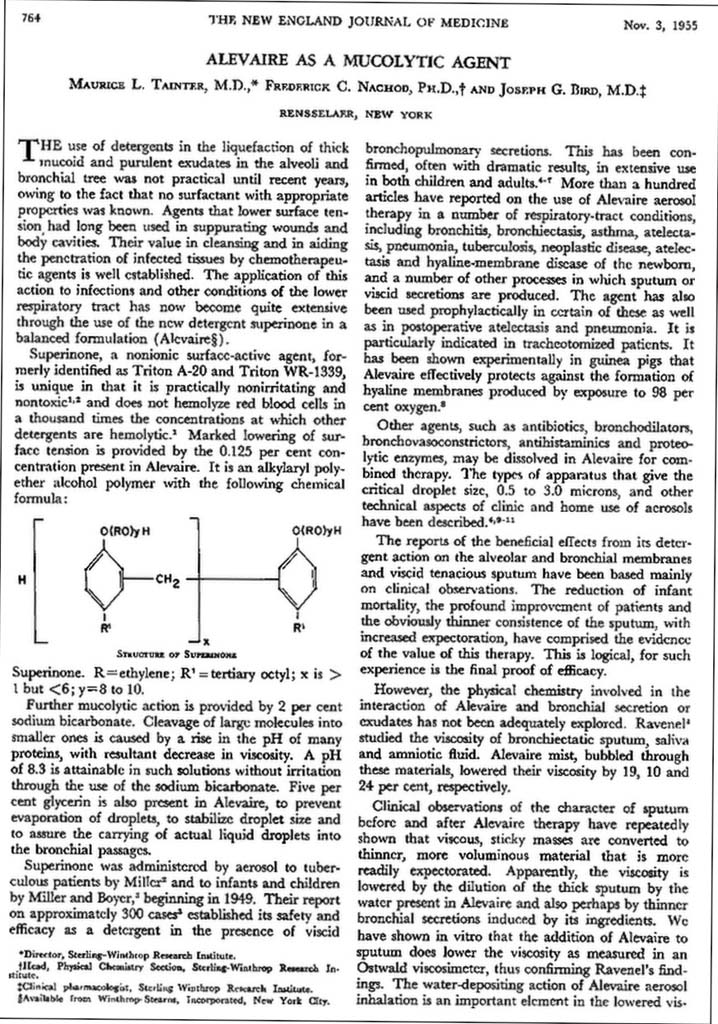

1955 Alevaire article
The article "Alevaire as a Mucolytic Agent" by M.L. Tainter et al appeared in the November 3, 1955 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
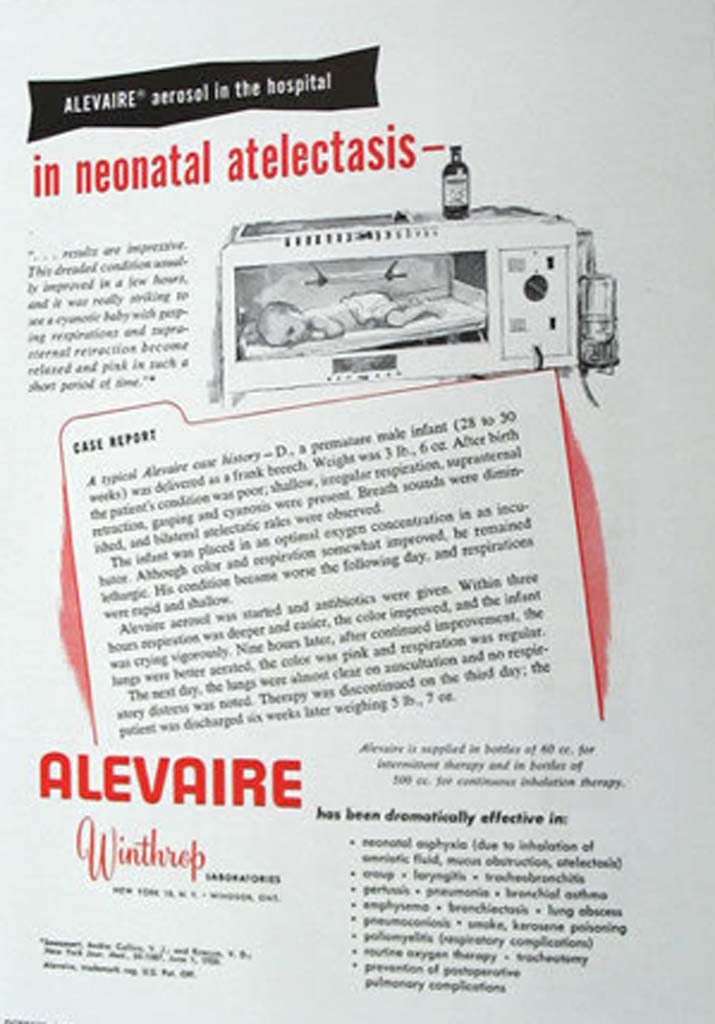

Alevaire
In this 1956 ad, aerosolized Alevaire was recommended for the treatment of neonatal atelectasis. Among other disorders, the ad claimed that Alevaire was effective in the treatment of bronchial asthma, pertussis, pneumonia, pulmonary complications of polio, croup, emphysema, kerosene poisoning, bronchiectasis, and lung abcess.


Alevaire
This ad for Alevaire is from the December 1959 issue of the INHALATION THERAPY journal .
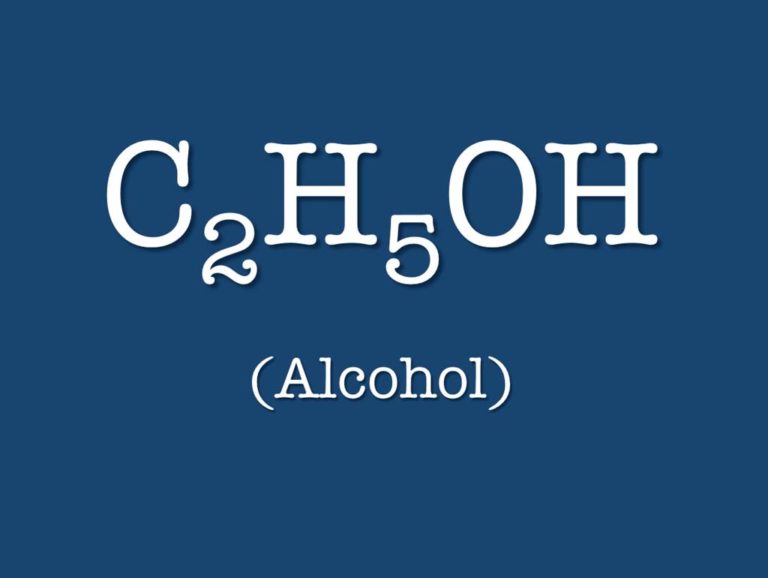

Alcohol
In the early 1950s, diluted alcohol-water mixtures were nebulized and administered to patients with acute pulmonary edema. This practice continued into the 1970s.


Norisodrine sulfate
Norisodrine (isoproterenol sulfate) was administered as a dry powder utilizing the Aerohaler as the delivery device. This ad appeared in the September 1958 issue of the INHALATION THERAPY journal.

1957 Riker's ad
This 1957 ad from Riker promoted their first pMDIs which contained either isoproterenol or epinephrine.
Image from Hardluckasthmablogspot


Isuprel Mistometer
The Isuprel Mistometer contained 15 mL of an isoproterenol hydrochloride solution in a pressurized canister.
Image from Felix Khusid
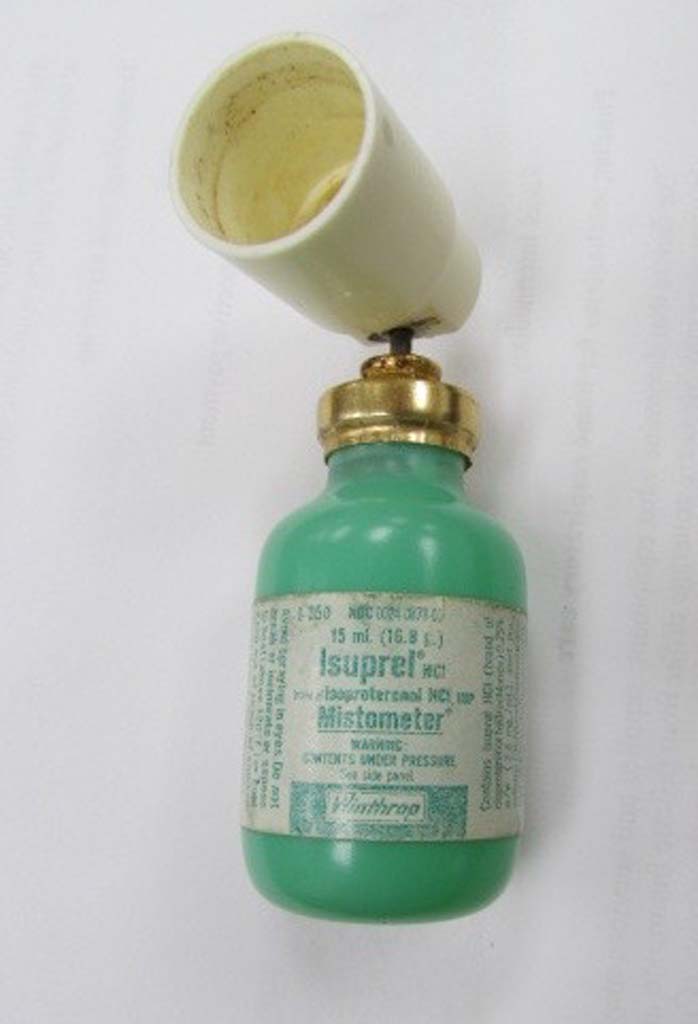

Isuprel Mistometer
An Isuprel Mistometer is shown.
Image from Kerry George


Isuprel Mistometer
The box for the Isuprel Mistometer is shown.
Image from Felix Khusid


1960s
Inhalation solutions and pMDIs from the 1960s are featured.


Tergemist
This ad, from the the October 1960 issue of the INHALATION THERAPY journal, features Tergemist.
Tergemist was described as a mucolytic aerosol solution containing "a detergent, potassium iodide, and distilled water."
Tergemist was described as a mucolytic aerosol solution containing "a detergent, potassium iodide, and distilled water."
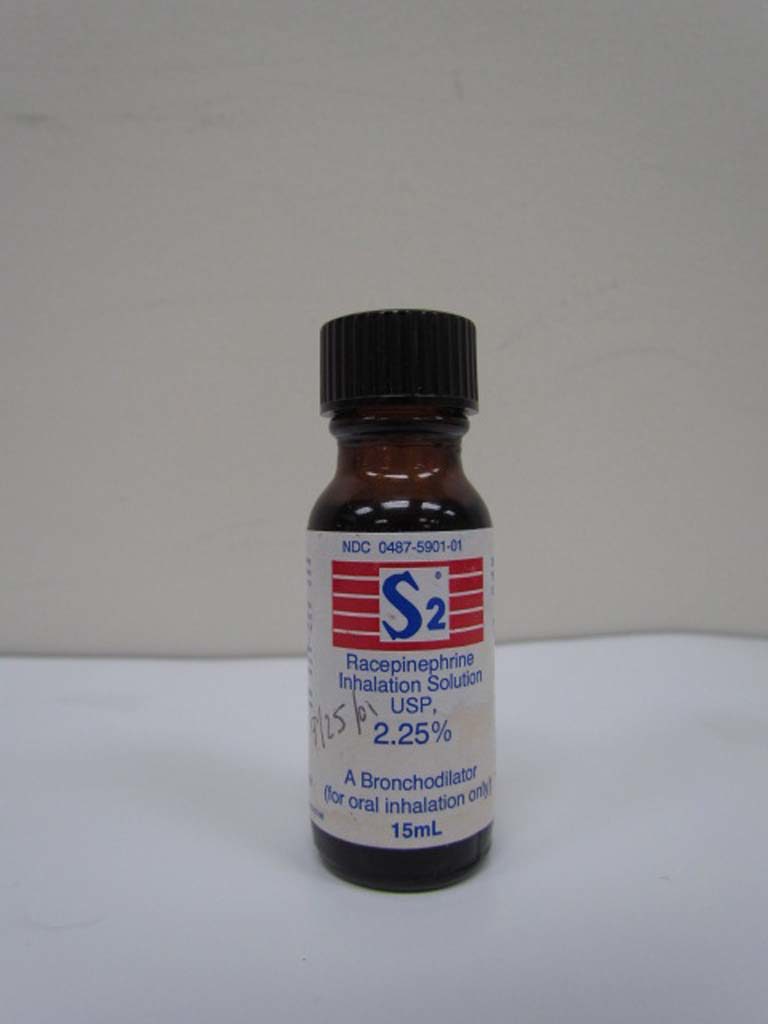


S2
Racemic epinephrine (2.25%), which was trademarked in 1962, is shown.
Image from Kerry George
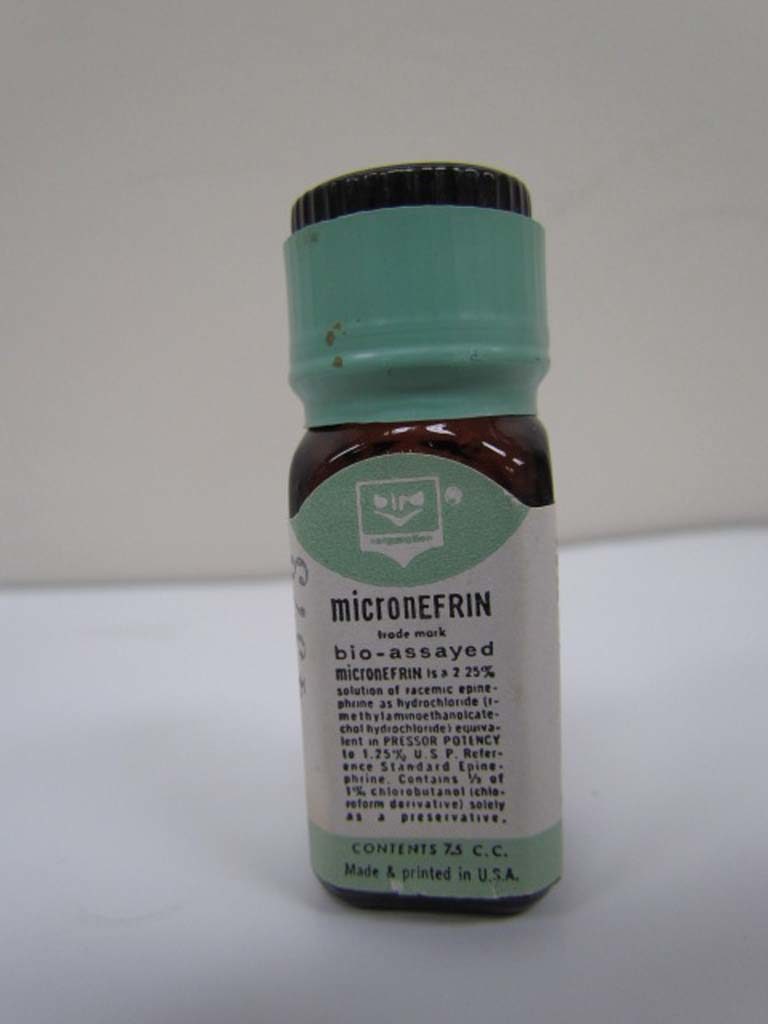
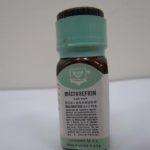
Micronefrin
Micronefrin (racemic epinephrine 2.25%) was trademarked in 1961 by the Bird Corporation.
Image from Kerry George

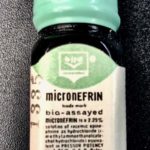
Micronefrin
Micronefrin (2.25% solution of racemic epinephrine). It also contained 1/2 of 1% chlorobutanol, a chloroform derivative, as a preservative agent.
Image from Felix Khusid


Micronefrin
The box for the 7.5 mL bottle of Micronefrin, a racemic epinephrine solution, from Bird Corporation is shown.
Image from Felix Khusid

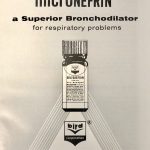
Micronefrin Pamphlet
Micronefrin (racemic epinephrine) was trademarked in 1961 by the Bird Corporation. The drug insert pamphlet is shown.
Image from Felix Khusid

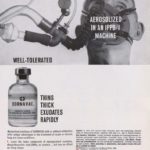
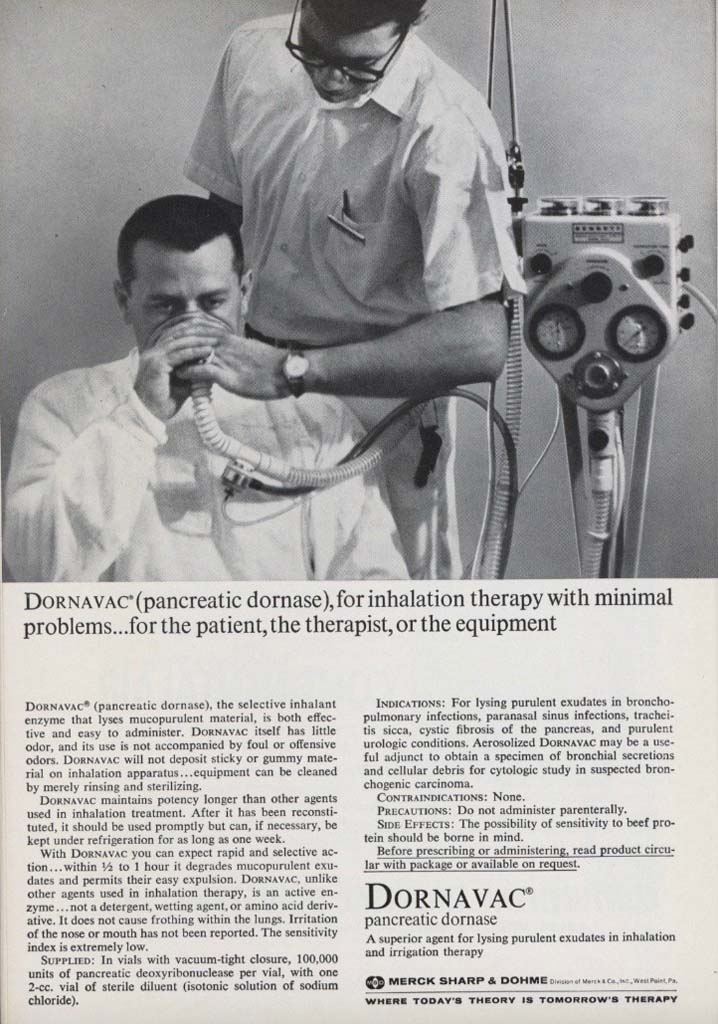
Dornovac
Dornovac (pancreatic dornase) was featured in this ad in the April 1963 issue of the INHALATION THERAPY journal.
Dornovac
Dornovac (pancreatic dornase) is featured in this 1965 ad from the October 1965 issue of the INHALATION THERAPY journal.
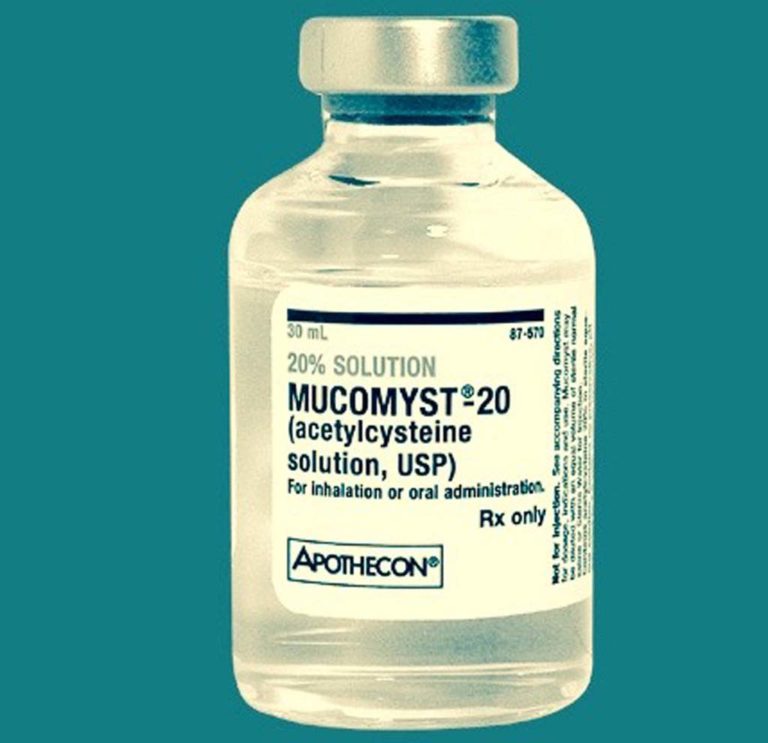
1963 Mucomyst approved
Mucomyst (acetylcysteine) was introduced in 1963 and was offered in 10% and 20% solutions.


Vapo-N-Iso
Vapo-N-Iso was a 0.5% solution of isoproterenol distributed by the U.S. Vitamin and Pharmaceutical Corporation of New York.
Image from Felix Khusid


Vapo-N-Iso
Vapo-N-Iso contained a 0.5% solution of isoproterenol HCl.
It was trademarked in 1963.
It was trademarked in 1963.
Image from Felix Khusid

Isuprel ad
This ad for Isuprel appeared in a late 1960s issue of the INHALATION THERAPY journal.


Bronkometer ad
Bronkometer's original formula of isoetharine, phenylephrine, and thenyldiamine is described in this ad.
Image from Felix Khusid


Bronkometer
The Bronkometer box states that it contains 10 mL of Dilabron (isoetharine ) mesylate 0.61% (w/w), phenylephrine HCl 0.125% (w/w) with saccharin, menthol, alcohol 30% (w/w) and with fluorochlorohydrocarbons as gaseous propellants. preserved with ascorbic acid 0.1% (w/w). The revised formula "does not contain the antihistaminic Thenyldiamince HCl."
Image from Felix Khusid


Bronkometer
Bronkometer 10 mL isoetharine mysylate and phenylephrine. This revised formula did not contain the antihistaminic Thenyldiamine HCl.
Image from Felix Khusid


Bronkosol
This ad for Bronkosol appeared in the April 1968 issue of INHALATION THERAPY.
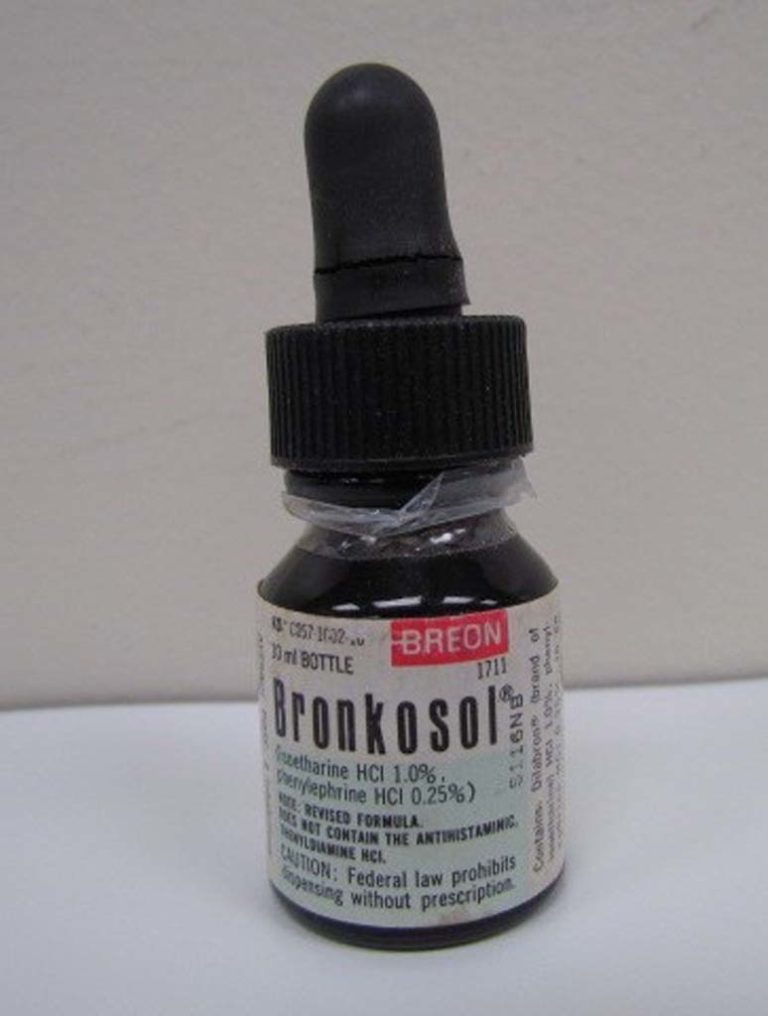


Bronkosol
Bronkosol (isoetharine and phenylephrine) was trademarked in 1966.
Image from Kerry George
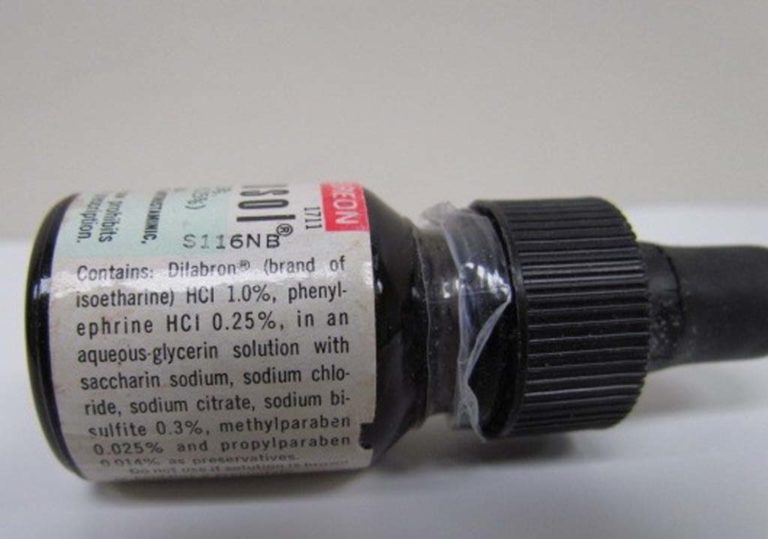

Bronkosol
The side label of a Bronkosol bottle is shown.
Image from Kerry George

Bronkosol label
The side label of a Bronkosol bottle is shown.
Image from Kerry George
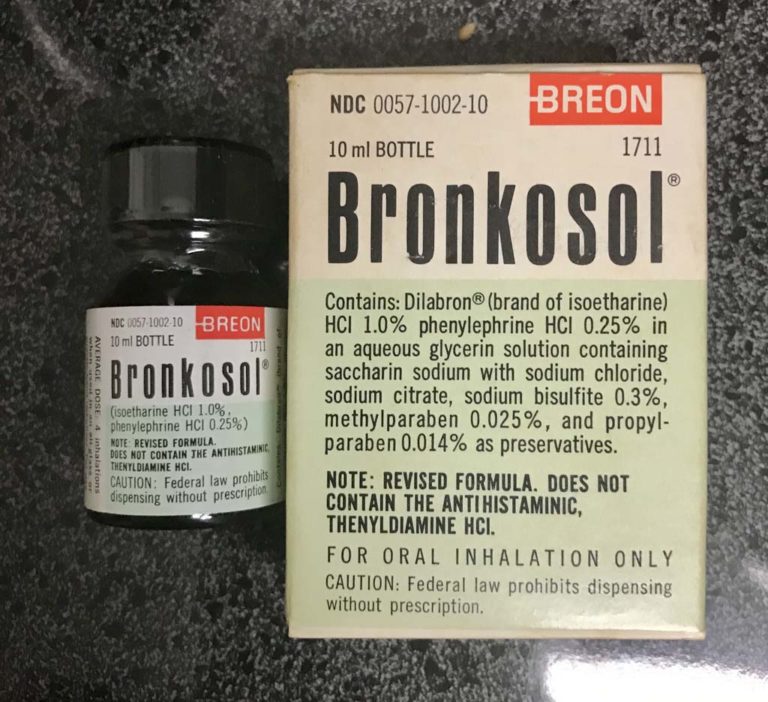
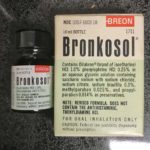
Bronkosol
Breon's revised formula of Bronkosol primarily contained Dilabron (Isoetharine HCl 1.0% and Phenylephrine HCl 0.25% in an aqueous glycerin solution with saccharin sodium with sodium chloride, sodium bisulfite, methylparaben, and propylparaben as preservatives.
Image from Felix Khusid


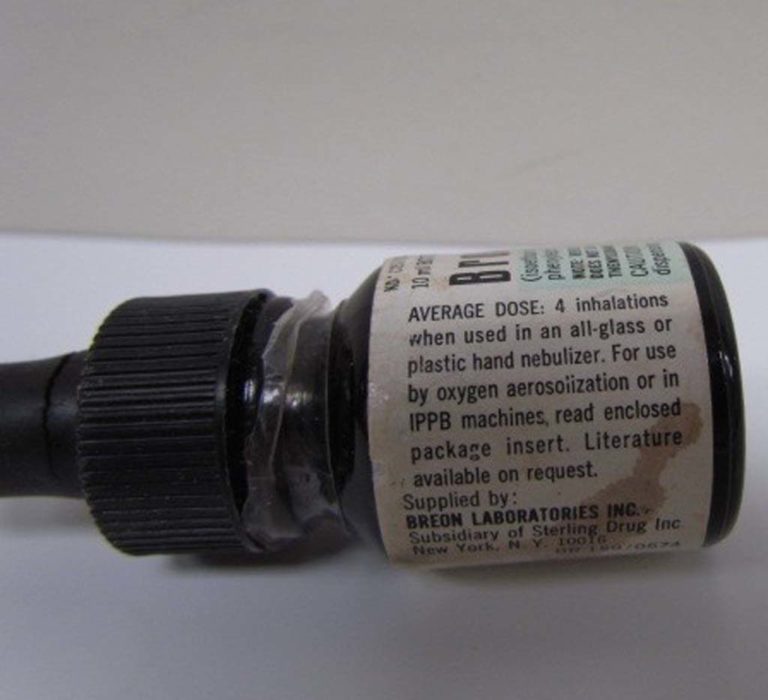
Bronkosol box
The reverse side of the box for Bronkosol indicated the average dose for an all glass or plastic hand nebulizer was 4 inhalations. It was also for use by "oxygen aerosolization or in IPPB machines."
Image from Felix Khusid


1970s
Inhalation solutions and MDIs from the 1970s are featured.
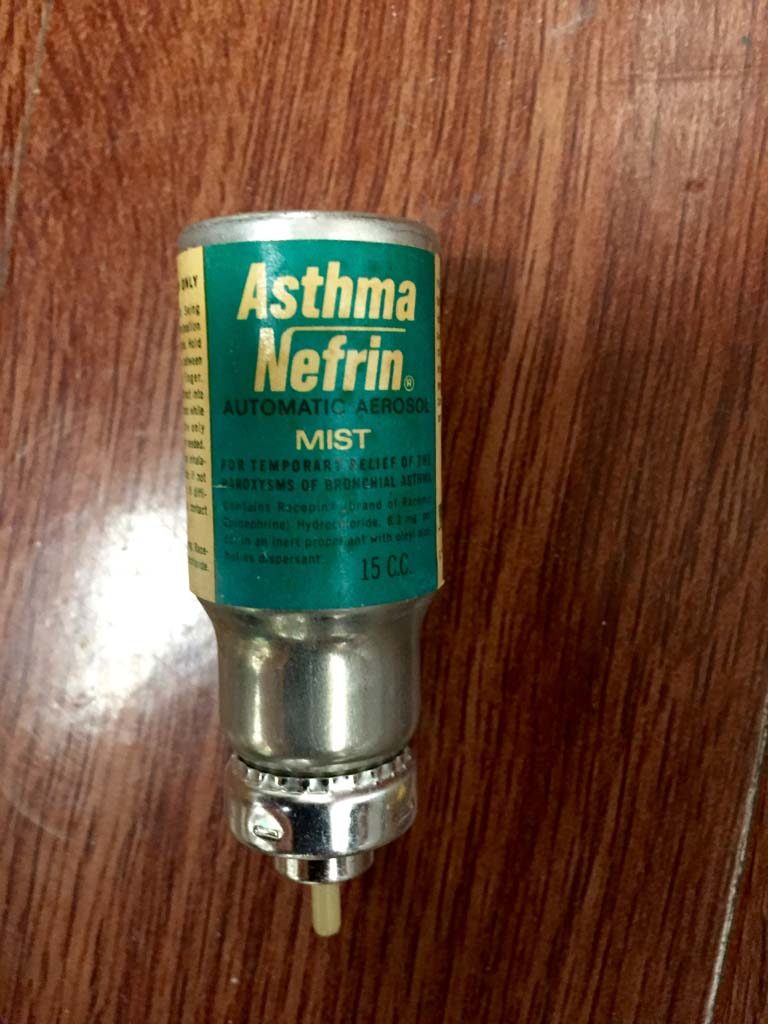
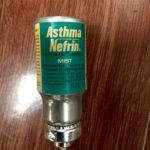
AsthmaNefrin MDI
The AsthmaNefrin automatic aerosol canister indicates it contained 15 c.c. of racemic epinephrine.
Image from Felix Khusid

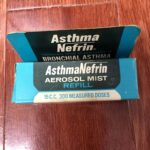
AsthmaNefrin
The box for AsthmaNefrin Aerosol Mist indicated that the refill contained 300 measured doses or 15 c.c. of racepinephrine.
Image from Felix Khusid
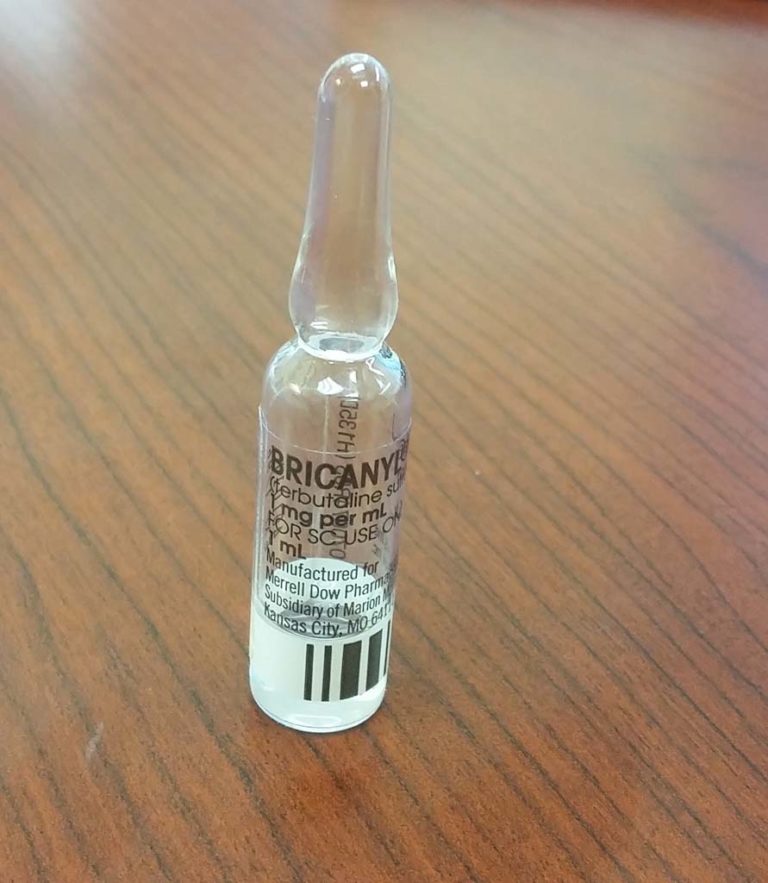


Bricanyl
Bricanyl (terbutaline sulfate) was approved by the FDA in 1974.
Image from Robert Johnson


Bronkometer
Breon's second revised formula for the Bronkometer, circa 1972, contained Isoetharine mesylate 0.61% (W/W) contained saccharine, menthol, alcohol 30% (W/W), and with fluorochlorohydrocarbons as gaseous propelllants. Preserved with ascorbic acid 0.1% (W/W)
Image from Felix Khusid
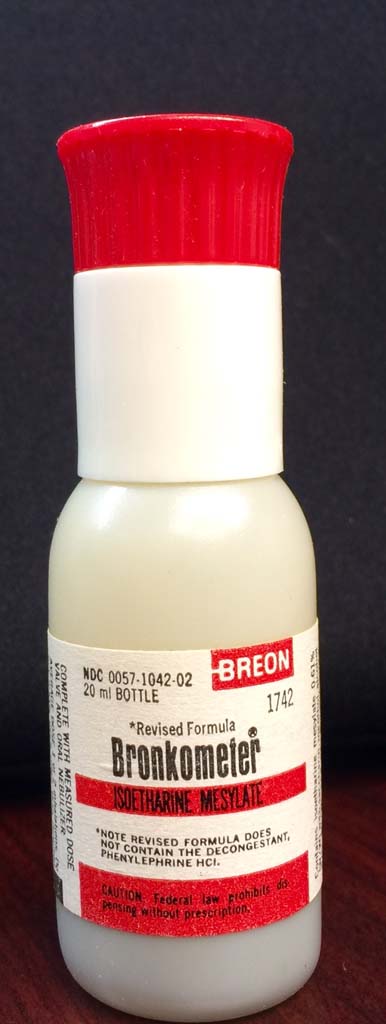

Bronkometer
Bronkometer (20 mL) bottle of Isoetharine mesylate
Image from Felix Khusid
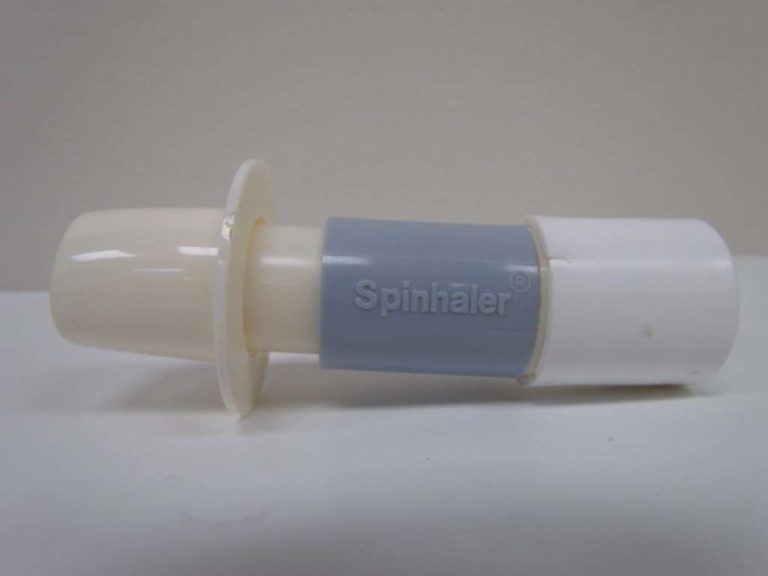


Intal Spinhaler
Intal (cromolyn sodium) was introduced in the early 1970s
. A capsule containing a dry powder of the agent, was inserted into the delivery device called the Spinhaler. The capsule was pierced and the powder was released and delivered to the patient on inspiration.
. A capsule containing a dry powder of the agent, was inserted into the delivery device called the Spinhaler. The capsule was pierced and the powder was released and delivered to the patient on inspiration.
Image from Kerry George
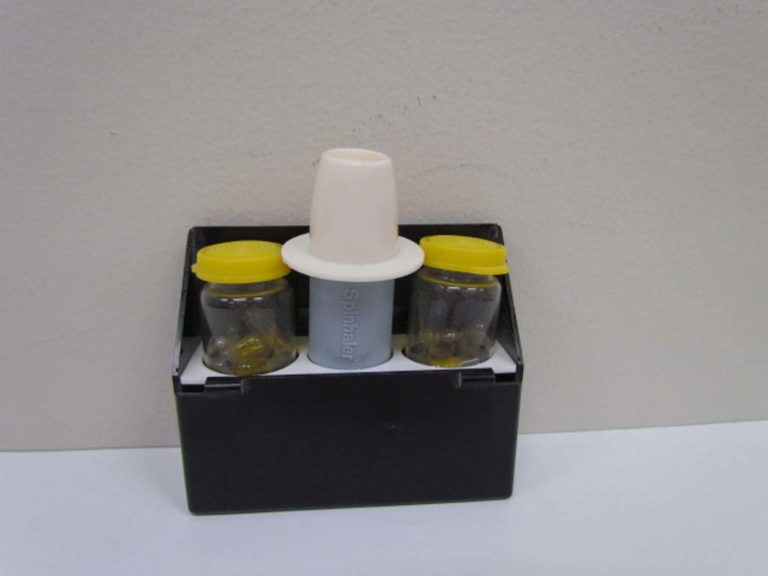


Intal Capsules and Spinhaler
An Intal Spinhaler and Intal capsules are shown.
Image from Kerry George
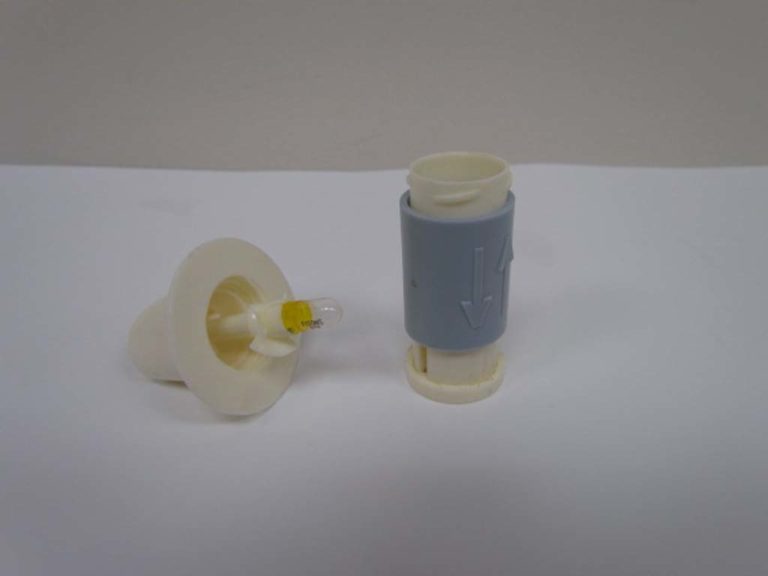


Intal Spinhaler
The Spinhaler is shown disassembled with the Intal capsule in place.
Image from Kerry George
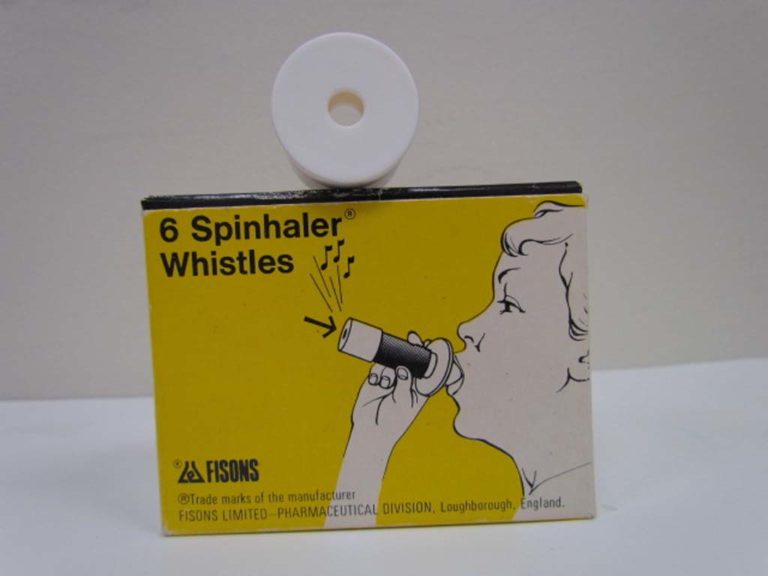
Spinhaler Whistles
A whistle attachment could be added to the Spinhaler and would sound when correct breathing techniques was used.
Image from Kerry George


1980s
Inhalation solutions and MDIs from the 1980s are featured.
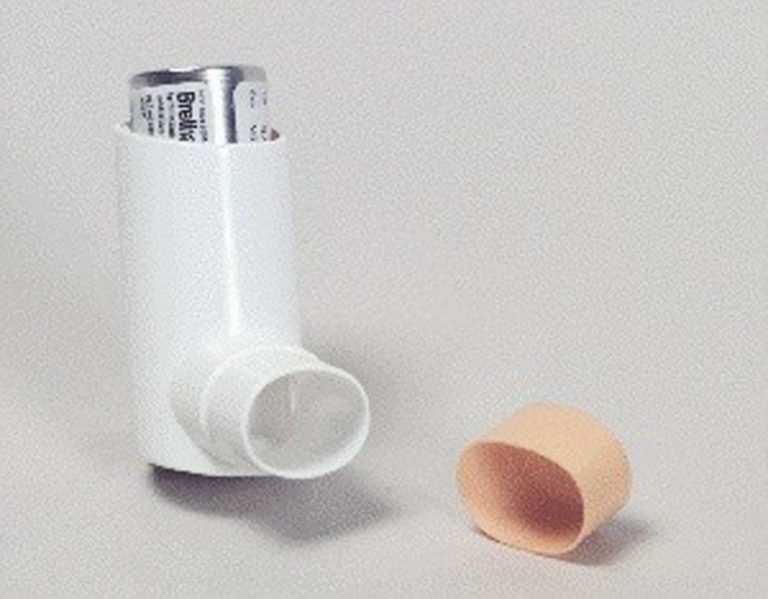

Brethaire
Brethaire (terbutaline sulfate) was supplied as an MDI. It was approved by the FDA in 1984.


Brethancer
The Brethancer was designed for use with the Brethaire MDI.
Image from Felix Khusid


Brethancer spacer
In 1984, the Brethancer spacer by Geigy was marketed for use with the Brethaire (terbutaline) MDI.
Image from Felix Khusid
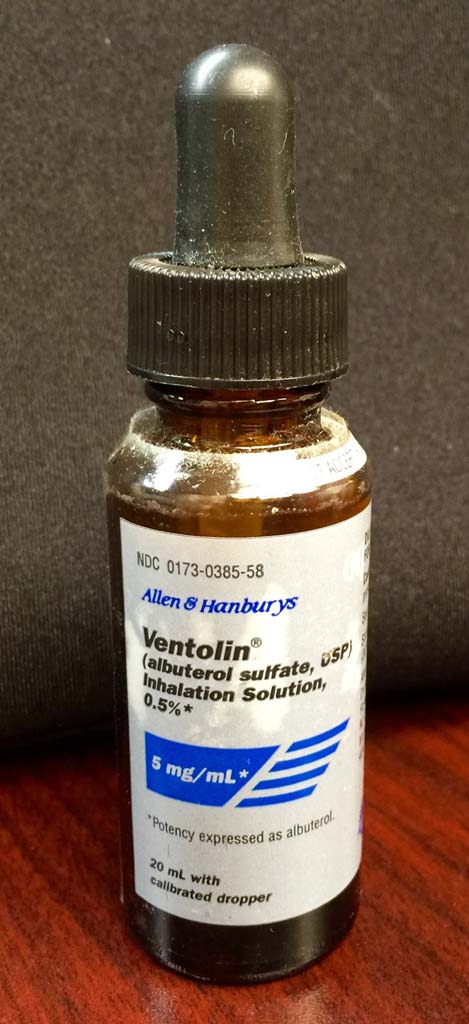
Ventolin
Allen and Hanbury's Ventolin (Albuterol sulfate) inhalation solution (0.5%)
Ventolin was approved by the FDA in 1987.
Ventolin was approved by the FDA in 1987.
Image from Felix Khusid
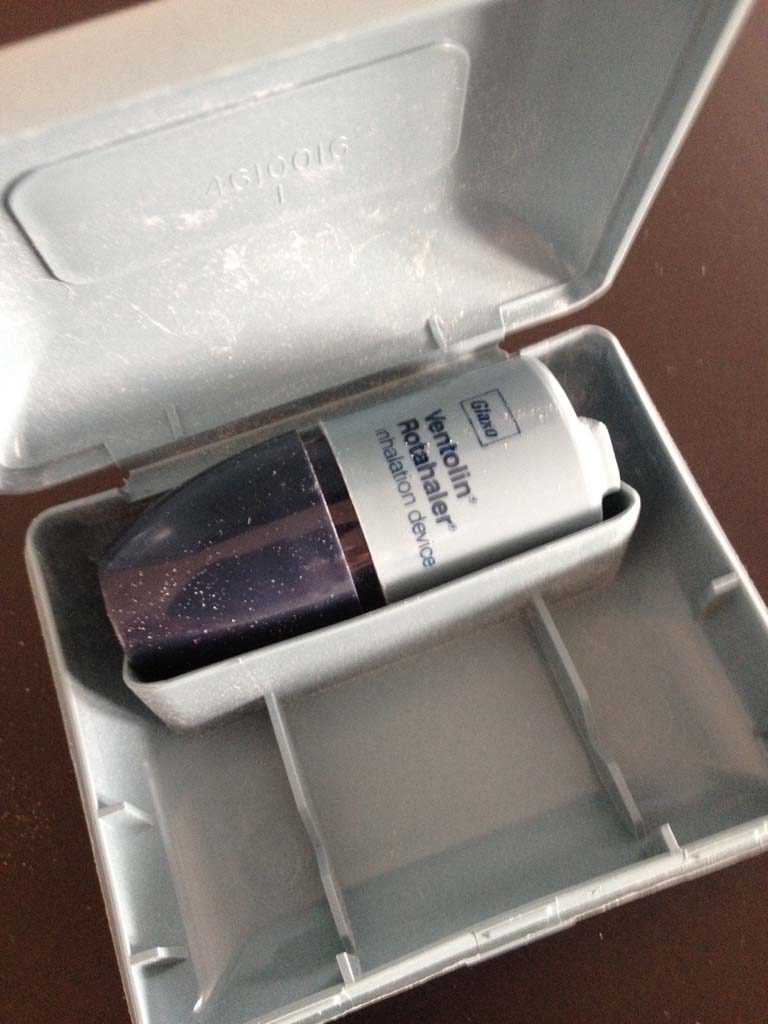


Ventolin Rotahaler
A Ventolin Rotahaler is shown in its carrying case.
Image from Wendy Dunlop
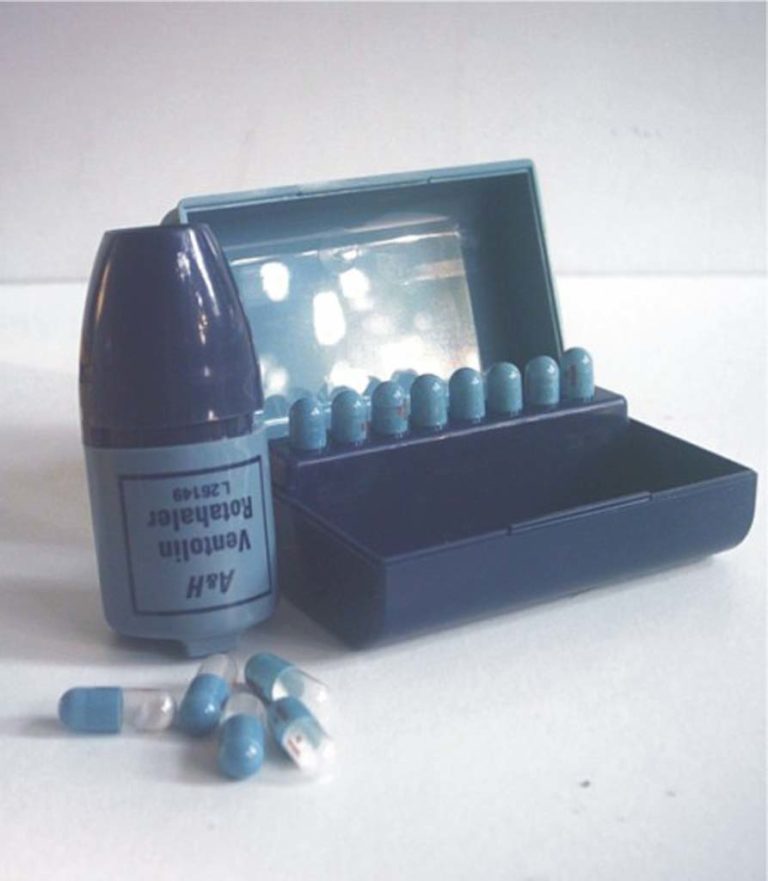


Ventolin Rotahaler
A Ventolin Rotahaler and Ventolin Rotacaps capsules are shown.
Image from Hardluck Asthma
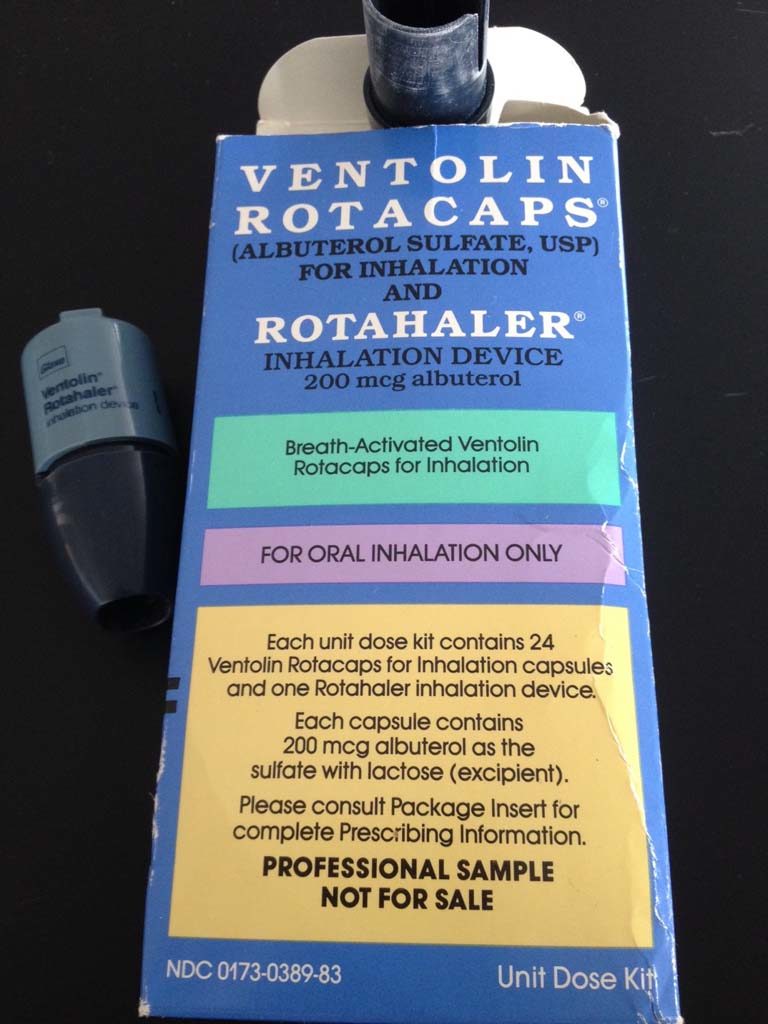

Ventolin Unit Dose Kit
The unit dose kit consisted of a Rotahaler and 24 Ventolin (albuterol sulfate) Rotacaps capsules.
Image from Wendy Dunlop


Images to share?
Please follow the instructions to share images for this gallery.